Hair Loss
Hair loss affects a wide range of people regardless of where they come from, who they are, or what they have. As we get older it’s common to start experiencing hair loss which can take a big toll on their confidence, how they are socially, and their self-esteem. But luckily there are hair restoration solutions to override the effects of hair loss or hair thinning.
Understanding Hair Loss
Androgenic alopecia is the scientific name for the genetic predisposition in anyone for pattern baldness. Genetic hair loss in men is often referred to as Male Pattern Baldness (MPB) and is the cause of thinning hair in over 95% of patients who seek treatment. MPB occurs in predictable stages, and is relentlessly progressive. Usually the earlier in life hair loss begins the more advanced the pattern will ultimately become.
In MPB, the hairs on the top of the scalp have a genetic sensitivity to the male hormone testosterone (DHT). The hairs on the sides and back of the scalp do not possess this sensitivity to DHT and therefore are not affected. For this reason hairs removed from the sides and the back (Donor Hair) will maintain their genetic predisposition when transplanted and continue to grow when moved to the top of the scalp where hair loss has occurred.
Hair loss in females is less predictable. The hair loss tends to be more diffuse creating a more generalized thinning effect throughout the entire scalp. Fewer medical and surgical options are available for these patients.
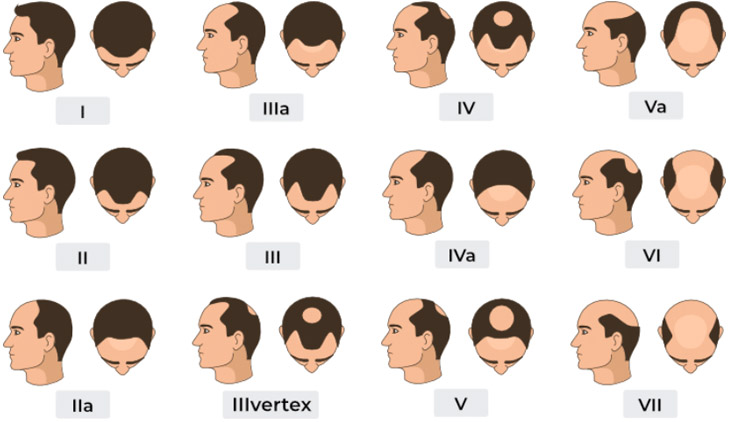
7 Stages of Hair Loss
Causes for Hair Loss
As stated earlier, people who develop this type of hair loss, which is the most common cause of hair loss worldwide. In men, it’s called male pattern hair loss. Women get female pattern hair loss. Regardless of whether it develops in a man or women, the medical term is androgenic alopecia or simply genetic hair loss.
No matter which term you use, it means that you’ve inherited genes that cause your hair follicles (what each hair grows out of) to shrink and eventually stop growing hair. Shrinking can begin as early as your teens, but it usually starts later in life.
In women, the first noticeable sign of hereditary hair loss is usually overall thinning or a widening part.
When a man has hereditary hair loss, the first sign is often a receding hairline or bald spot at the top of his head.
Is Age a Factor in Hair Loss?
Although aging is not a cause for hair hair loss, with aging most people notice some hair loss because hair grows slower. At some point, hair follicles stop growing hair, which causes the hair on our scalp to thin. Hair also starts to lose its color. A woman’s hairline may naturally starts to recede.
Types of Hair Loss
-
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata (spotty hair loss) is a disease that develops when the body’s immune system attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss. You can lose hair anywhere on your body, including your scalp, inside your nose, and in your ears. Some people lose their eyelashes or eyebrows. There are medical treatment and it resolves itself overtime.
-
Cancer Treatment
If you receive chemotherapy or have radiation treatment to your head or neck, you may lose all (or most of) your hair within a few weeks of starting treatment. Hair usually starts to regrow within months of finishing chemotherapy or radiation treatments to the head or neck. Dermatologists can offer medication to help hair grow back more quickly.
-
Treated Hair
If you color, perm, or relax your hair, you could be damaging your hair. Over time, this damage can lead to hair loss.
-
Traction Alopecia
Traction alopecia is hair loss due to pulling hair into tight hairstyles, which causes it to break and come loose. Often referred to as hair loss on the edges traction alopecia is caused by tight buns or ponytails, braids, cornrows and hair extensions. If the traction damage has been long enough there can be permanent hair loss.
-
Hormonal Imbalance
A common cause of this imbalance is polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). It leads to cysts on a woman’s ovaries, along with other signs and symptoms, which can include hair loss. Stopping some types of birth control pills can cause a temporary hormonal imbalance. Women who develop a hormonal imbalance can develop thinning hair (or hair loss) on their scalp.
-
Scalp Infection
A scalp infection can lead to scaly and sometimes inflamed areas on your scalp. You may see what look like small black dots on your scalp. These are actually stubs of hair. Some people develop a bald spot.
-
Medications
A possible side effect of some medications is hair loss. If you think a medication is causing your hair loss, ask the doctor who prescribed it if hair loss is a possible side effect. It’s essential that you do not stop taking the medication before talking with your doctor. Abruptly stopping some medications can cause serious health problems.
-
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a condition where the hair remains in the telogen (natural shedding) phase of the growth cycle. This causes more hair to fall out, sometimes in handfuls. Telogen effluvium is usually a temporary condition that resolves over time. It is advisable to see a doctor to find out the cause.
-
Scalp Psoriasis
Many people who have plaque psoriasis develop psoriasis on their scalp at some point. This can lead to hair loss.
-
Scarring Alopecia
This condition develops when inflammation destroys hair follicles. Once destroyed, a hair follicle cannot grow hair. Diverse conditions can cause this. The medical name for this group of conditions is cicatricial alopecia.
-
Thyroid Disease
If you have a problem with your thyroid, you may see thinning hair. Some people notice that their hair comes out in clumps when they brush it.
