Male Hair Loss: Reclaim Your Confidence
Are you struggling with male pattern baldness? You’re not alone. At Katona Hair, we understand the impact that hair loss can have on your confidence and self-esteem. That’s why we offer effective solutions to help you regain a full head of hair and feel your best.
Our team of experts specializes in addressing male hair loss using advanced techniques and state-of-the-art technology. Rather than letting hair loss dictate your life, take control and explore the options available to you.
With our personalized approach, we tailor each treatment plan to meet your specific needs and goals. Whether you’re interested in non-surgical options like medication or are considering hair transplant surgery, we’re here to guide you every step of the way.
Don’t let hair loss hold you back any longer. Take the first step towards a more confident you by scheduling a consultation with our experienced team today. Together, we’ll develop a plan to restore your hair and your confidence.
Understanding the Causes of Hair Loss In Men
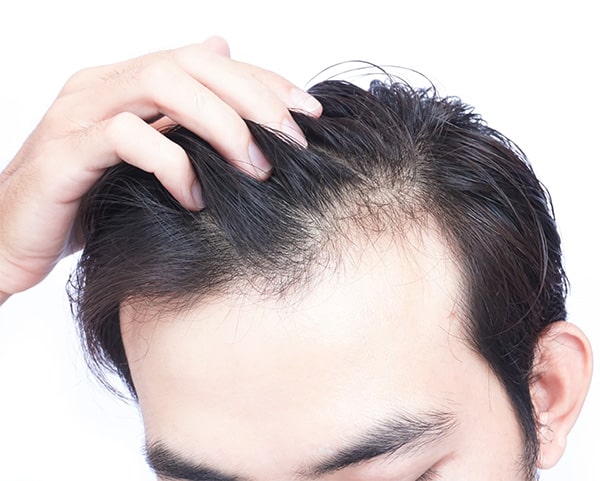 Men often notice hair loss as they age, but it can stem from various factors. These include genetic predisposition, illnesses, and medications. To pinpoint the exact cause, consulting with a certified hair loss expert like Dr. Katona, accredited by the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery, is crucial.
Men often notice hair loss as they age, but it can stem from various factors. These include genetic predisposition, illnesses, and medications. To pinpoint the exact cause, consulting with a certified hair loss expert like Dr. Katona, accredited by the American Board of Hair Restoration Surgery, is crucial.
Additionally, lifestyle factors can play a significant role in male hair loss. Stress, exposure to chemicals or UV rays, smoking, and alcohol consumption can all trigger or exacerbate hair loss. Identifying and addressing these factors early on can help in managing and mitigating hair loss.
Male Pattern Hair Loss (Androgenetic hair loss)
This type of hair loss predominantly affects men, impacting 50-70% of males. It occurs when scalp hairs undergo miniaturization, where thick terminal hairs are gradually replaced by finer, thinner versions.
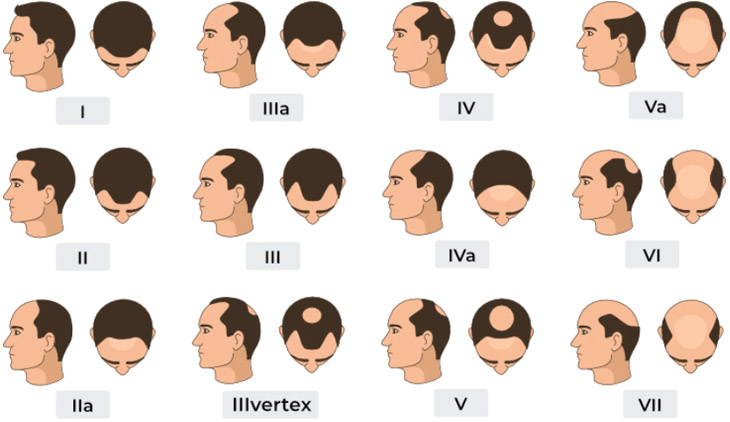
Familial Hair Loss Pattern
Hair loss often has a familial pattern. The severity of male pattern hair loss is typically assessed using the Hamilton-Norwood Scale, which evaluates the extent of hair loss. Primarily, men experience hair loss in the frontal hairline and vertex (crown) of the scalp. While distressing, there are numerous medical and surgical treatment options available.
Hair Loss Medications
Currently, the FDA has approved only two medications for male pattern hair loss. Additionally, several low-level light therapy (LLLT) devices have received FDA clearance for treating androgenetic alopecia. Hair restoration surgery provides patients with a more permanent and dramatic solution. Camouflaging agents are also popular and effective in managing hair loss.
Temporary Hair Loss in Men
Temporary hair thinning can result from several medical conditions, with hypothyroidism commonly causing this issue in men. Treating this condition usually reverses the temporary hair thinning, emphasizing the importance of consulting a physician to identify the underlying cause. Other potential triggers for temporary baldness include exposure to general anesthesia, high fever, physical trauma, and chemotherapy.
Elevated stress levels can also contribute to temporary baldness. While the exact mechanism behind this type of hair loss is not fully understood, emotional and hormonal factors can lead to excessive shedding. Typically, regrowth occurs within 3-4 months with temporary hair loss.
Types of Male Hair Loss
Telogen Effluvium Hair Loss
This condition involves diffuse hair shedding triggered by major physiologically stressful events. Examples include high fever, crash dieting, general anesthesia, prolonged illness or hospitalization, hormonal or thyroid disorders, nutritional deficiencies, and certain medications. Major life events such as the death of a loved one, divorce, or financial loss can also lead to telogen effluvium.
Thyroid Disorder
Untreated hyper- or hypothyroidism can result in hair shedding and eyebrow thinning or loss.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Hair shedding has been linked to low levels of iron, zinc, and vitamin D in medical literature.
Hair Loss From Medications
Certain medications like high-dose vitamin A, isotretinoin, and specific cardiovascular drugs such as beta-blockers (metoprolol, propranolol) and low molecular weight heparin (and less commonly warfarin) have been associated with hair shedding. Discontinuing the drug for 3-6 months to observe if shedding resolves, then restarting the drug to see if shedding recurs, is necessary to confirm medication-related hair loss. This evaluation process can take 6-12 months, and patients should consult their doctor before stopping any medication to avoid potential risks.
Anagen Effluvium
This type of hair loss occurs due to a disruption of the hair growth cycle during its actively growing (anagen) phase, often after certain chemotherapy treatments. While hair loss is typically temporary, some individuals may experience scanty regrowth or permanent changes in hair texture or caliber. Concurrent use of topical minoxidil has been shown to delay hair loss and promote regrowth in some cases.
Alopecia Areata
An autoimmune form of hair loss characterized by small round-to-oval patches on the scalp, alopecia areata can affect larger areas, eyebrows, eyelashes, and body hair. It results from an attack on hair follicles by lymphocytes (T-cells), sometimes targeting pigment cells, leading to white regrowth. Treatment options range from topical and intralesional corticosteroids to systemic immunosuppressive therapies such as methotrexate or prednisone, with increasing use of JAK inhibitors. Many cases resolve spontaneously without treatment.
Congenital Triangular Alopecia
Localized to the frontotemporal scalp, this form of alopecia typically appears in early childhood, presenting in various shapes along the frontal and lateral hairlines. There is no inflammation or scarring, but scalp pathology reveals normal follicle numbers with miniaturization. Hair restoration surgery is the mainstay of therapy for adults.
